Soft Tissue Segmentation using Image Dataset in Python Projects
Soft Tissue Segmentation using Image Dataset in Python Projects
Soft Tissue Segmentation using Image Dataset in Python Projects
Abstract
Soft tissue segmentation is a critical step in medical image analysis, aiding in diagnosis, surgical planning, and treatment monitoring for various medical conditions. The project Soft Tissue Segmentation using Image Dataset in Python Projects focuses on developing an automated system that segments soft tissues from medical images such as MRI or CT scans using deep learning techniques. Python is chosen as the development platform for its comprehensive libraries for image processing, deep learning, and visualization, including OpenCV, TensorFlow, Keras, SimpleITK, and NumPy. The system preprocesses medical images to enhance quality, normalize intensity, and remove noise, then applies convolutional neural networks (CNNs) or U-Net-based architectures for pixel-level segmentation. Automated segmentation of soft tissues improves diagnostic accuracy, reduces manual workload, and supports clinicians in treatment planning.
Existing System
Existing soft tissue segmentation methods often rely on manual delineation by radiologists, which is time-consuming, subjective, and prone to inter-observer variability. Traditional image processing techniques such as thresholding, region-growing, and edge detection can segment tissues but struggle with complex anatomical structures, low contrast, or overlapping organs. Some machine learning approaches using handcrafted features have been attempted, but they lack generalization across diverse datasets and fail to capture intricate spatial relationships. As a result, existing systems are limited in accuracy, efficiency, and scalability for clinical applications.
Proposed System
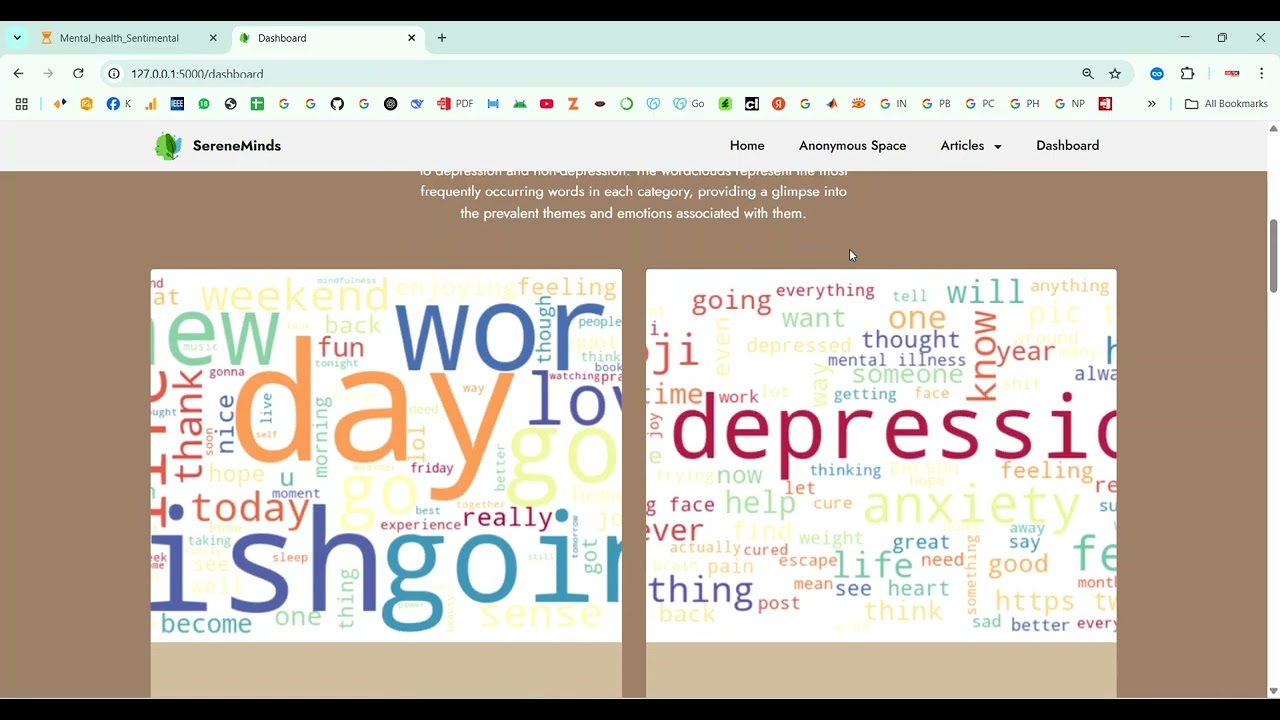
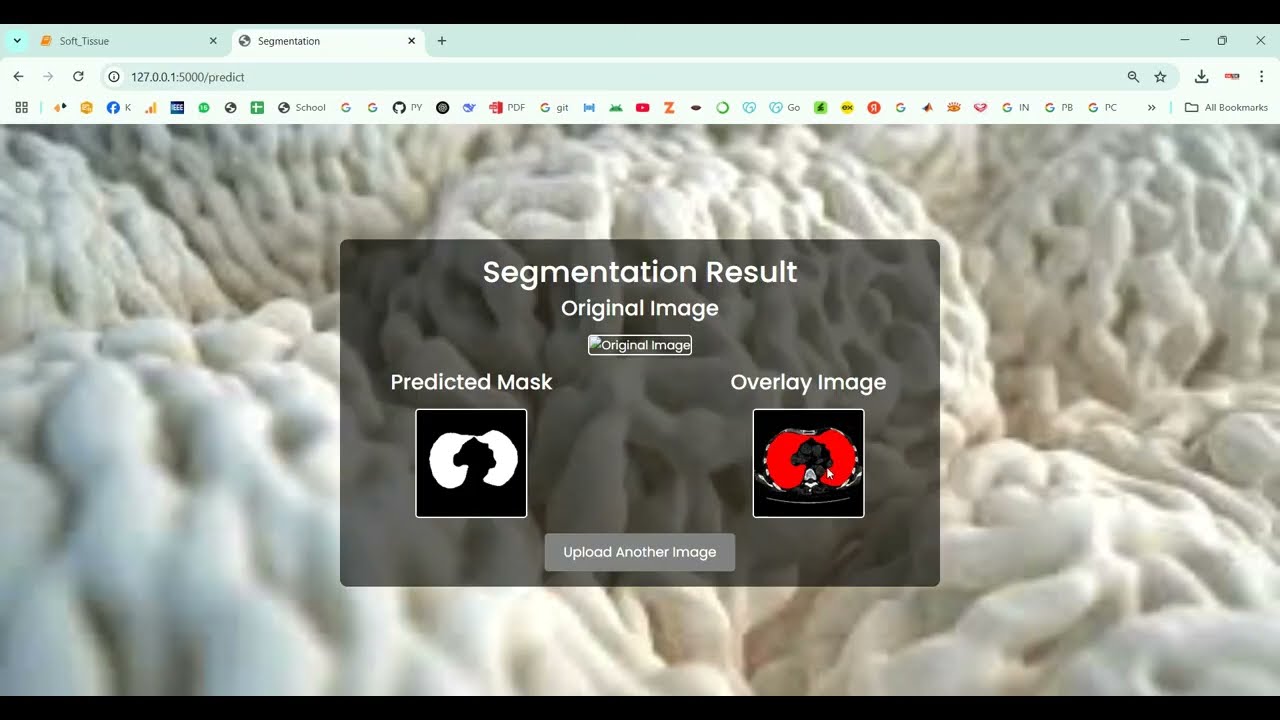
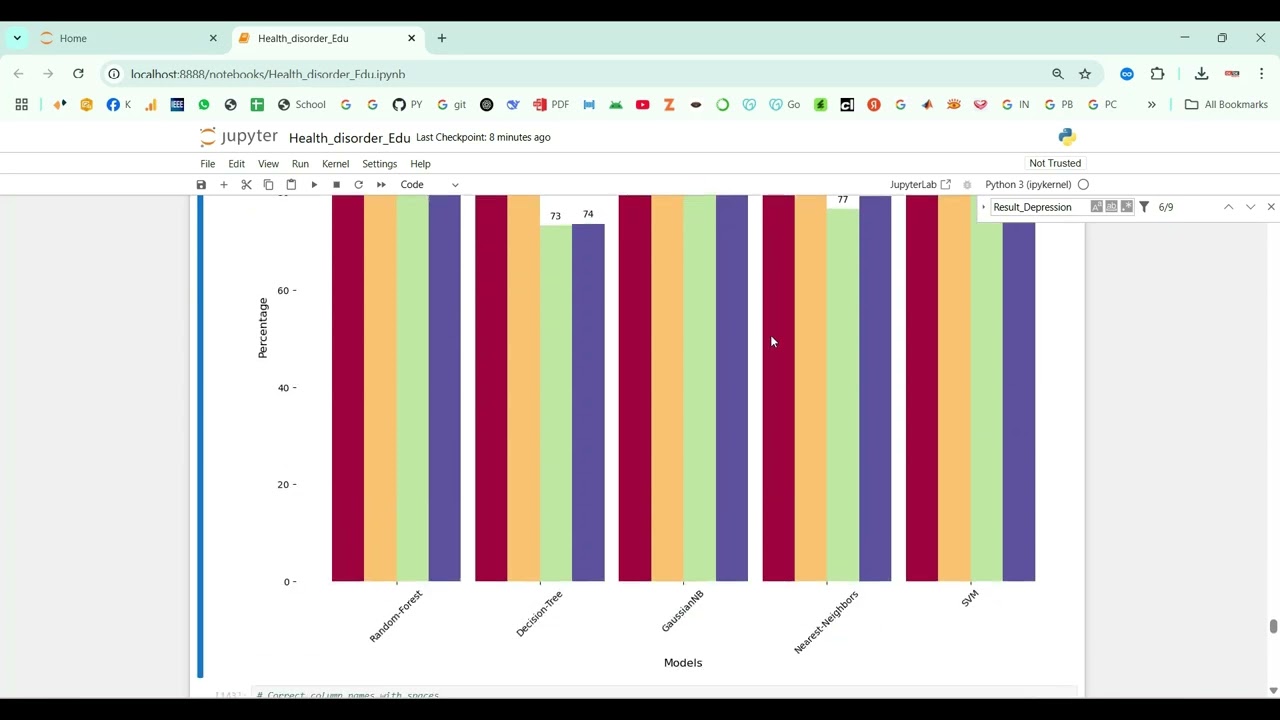
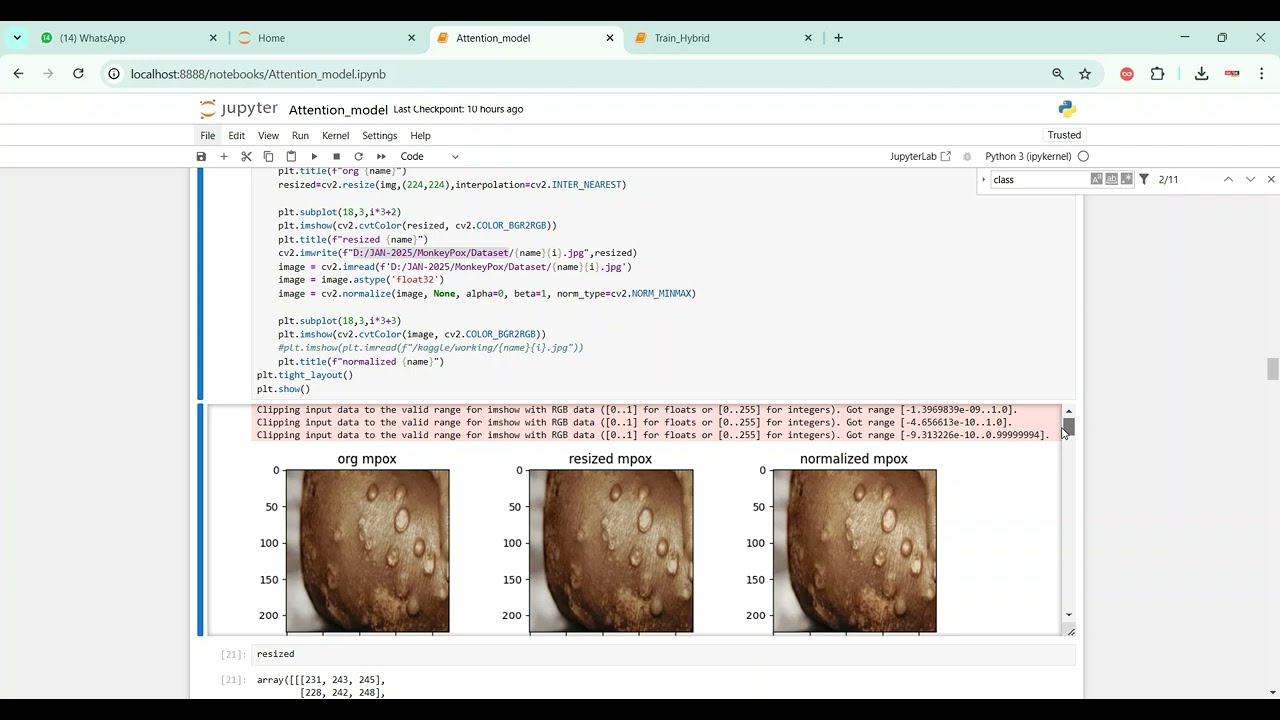
The proposed system introduces a Python-based deep learning framework for automated soft tissue segmentation. Preprocessing steps include denoising, intensity normalization, resizing, and contrast enhancement to improve image quality. CNN or U-Net architectures are trained on annotated medical image datasets to perform precise pixel-level segmentation of soft tissues. Data augmentation techniques such as rotation, flipping, and scaling are applied to enhance model generalization across different datasets. The system outputs segmented tissue masks overlayed on original images for visualization and clinical analysis. Performance is evaluated using metrics such as Dice coefficient, Intersection over Union (IoU), precision, and recall. By leveraging deep learning for soft tissue segmentation, the system provides a scalable, reliable, and automated solution that enhances diagnostic efficiency, supports treatment planning, and reduces the burden on healthcare professionals.
What's Your Reaction
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0